Rereading Alfred North Whitehead, one of my favorite philosophers, provides the context for the current debate over the wisdom of using the EPA’s amended transportation emissions model (Motor Vehicle Emission Simulator, or MOVES) for state-by-state analysis. He once indicated that, “There are no whole truths; all truths are half-truths. It is trying to treat them as whole truths that plays the devil.”
I am uncertain about Whitehead’s skepticism, if treated as an absolute. However, it does give pause when judging the use of an amended MOVES model, based mostly on advocacy research by the nonprofit group, the Coordinating Research Council (CRC). The CRC is funded by the oil industry, through the American Petroleum Institute (API), and auto manufacturers.
CRC was tasked by the EPA with amending MOVES and applying it to measure and determine the impact of vehicular emissions. The model and related CRC analysis was subject to comments in the Federal Register but the structure of the Register mutes easy dialogue over tough, but important, methodological disagreements among experts. Apparently, no refereed panel subjected the CRC’s process or product to critique before the EPA granted both its imperator and sent it out to the states for their use.
I am concerned that if the critics are correct, premature statewide use of the amended MOVES model will mistakenly impede development and use of alternative transitional fuels to replace gasoline, particularly ethanol, and negatively influence related federal, state and local policies and programs concerning the same. If this occurs, because of apparent mistakes in the model (and the data plugged into it), the road to significant use of renewable fuels in the future will be paved with higher costs for consumers, higher levels of pollutants and higher GHG emissions.
With some exceptions, the EPA has been a strong supporter of unbiased, nonpartisan research. Gina McCarthy, its present leader, is an outstanding administrator, like many of her predecessors, like Douglas Costle (I am proud to say that Doug worked with me on urban policy, way, way back in the sixties), Russell Train, Carol Browner, William Reilly, Christine Todd Whitman, Bill Ruckelshaus and Lee Thomas. No axes to grind; no ideological or client bias…only a commitment to help improve the environment for the American people. I feel comfortable that she will listen to the critics of MOVES.
The amended MOVES may well be the best thing since the invention of Swiss cheese. It could well help the nation, its states and its citizens determine the truths or even half-truths (that acknowledge uncertainties) related to gasoline use and alternative replacement fuels. But why the hurry in making it the gold standard for emission and pollutant analysis at the state or, indeed, the federal level, in light of some of the perceived methodological and participatory problems?
Some history! Relatively recently, the EPA correctly criticized CRC because of its uneven (at best) analytical approach to reviewing the effect of E15 on car engines. Paraphrasing the EPA’s conclusions, the published CRC study reflected a bad sample as well as too small a sample. Its findings, indicating that E15 had an almost uniform negative impact on internal combustion engines didn’t comport with facts.
The CRC’s study of E15 was, pure and simple, advocacy research. CRC reports generally reflect the views of its oil and auto industry funders and results can be predicted early on before their analytical efforts are completed. Some of its reports are better than others. But overall, it is not known for independent unbiased research.
The EPA’s desire for stakeholder involvement in up grading and use of MOVES to measure emissions is laudable. However it seems that the CRC was the primary stakeholder involved on a sustained basis in the effort. No representatives of the replacement fuel industry, no nonpartisan independent nonprofit think tanks, no government-sponsored research groups and no business or environmental advocacy groups were apparently included in the effort. Given the cast of characters (or the lack thereof) in the MOVES’ update, there’s little wonder that the CRC’s approach and subsequently the EPA’s efforts to encourage states to use the amended model have been and, I bet, will be heavily criticized in the months ahead.
Two major, well-respected national energy and environmental organizations, Energy Future Coalition (EFC) and Urban Air Initiative, have asked the EPA to immediately suspend the use of the MOVES with respect to ethanol blends. Both want the CRC/MOVES study and model to be peer reviewed by experts at Oak Ridge National Lab (ORNL), and the National Renewable Energy Lab (NREL). I would add the Argonne National Laboratory because of its role in administering GREET, The Greenhouse Gases, Regulated Emissions, and Energy Use in Transportation Model. Further, both implicitly argue that Congress should not use the CRC study and MOVES until the data and methodological issues are fixed. Indeed, before policy concerning the use of alternative replacement fuels is debated by the administration, Congress and the states both appear to want to be certain that MOVES is able to provide reasonably accurate estimates of emissions and market-related measurements, particularly with respect to ethanol and, as Whitehead would probably say, at least provide half-truths, or, as Dragnet’s Detective Jack Webb often said, “Just the facts, ma’am,” or at least just the half-truths, nothing but at least the half-truths.
What are the key issues upsetting the critics like the EFC and the Urban Air Initiative? Apart from the pedigree of the CRC and the de minimis roles granted other stakeholders than the oil industry, the CRC/MOVES model, reflects match blending instead of splash blending to develop ethanol/gasoline blends. Sounds like two different recipes with different products — and it is. Splash blending is used in most vehicles in the U.S. and generally is perceived as producing less pollution.
Let’s skip the precise formula. It’s complicated and more than you want to know. Just know that according to the letter sent to the EPA by the EFC and Urban Air Quality on Oct. 20th, the use of match blending requires higher boiling points for distillation, and these points, in turn are generally the worst polluting aromatic parts of gasoline. It noted that match blending, as prescribed by the MOVES, results in blaming ethanol for increased emissions rather than the base fuel. There is no regulatory, mechanical or health justification for adding high boiling point hydrocarbons to test fuels for purposes of measuring changes in vehicle tailpipe emissions, when ethanol is part of the fuel mixture. Independent investigations by automakers and other fuel experts confirm that the use of match blending in the study mistakenly attributed increased emission levels to ethanol rather than to the addition of aromatics and other high boiling hydrocarbons, thereby significantly distorting the model’s emission results. A peer-reviewed analysis, which will be published shortly, found that the degradation of emissions which can result is primarily due to the added hydrocarbons, but has often been incorrectly attributed to the ethanol.
The policy issues involved due to the methodological errors are significant. If states and other government entities, as well as fuel supply chain participants, use the model in its present form, they will mistakenly believe that ethanol’s emissions and pollutants are higher than reported in study after study over the past decade. The reported results will be just plain wrong. They will not even be half-truths, but zero truths. Distortions in decision making concerning the wisdom of alternative transitional replacement fuels, particularly ethanol, will occur and generate weaker ethanol markets and opportunities to build a strategic path to renewables. The EPA, rather than encourage use of the study and the model, should pull both back and suggest waiting until refereed review panels finish their work.

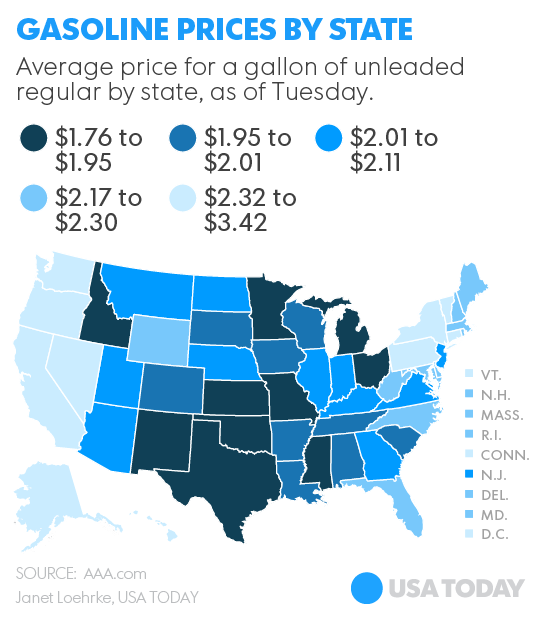
 Turn on your local news every night and you’ll need a sleeping pill to get some rest. The format and content is the same around the country: a lot of tragic crime — ranging from sexual harassment, robbery and shootings — for about ten minutes; local sports for about 5 minutes; what seems like ten minutes of intermittent advertising; silly banter between two or more anchors for two minutes; and a human-interest story to supposedly lighten up your day at the very end of the show — likely about a dog and cat who have learned to dance together or a two-year-old child who already knows how to play Mozart. You get the picture!
Turn on your local news every night and you’ll need a sleeping pill to get some rest. The format and content is the same around the country: a lot of tragic crime — ranging from sexual harassment, robbery and shootings — for about ten minutes; local sports for about 5 minutes; what seems like ten minutes of intermittent advertising; silly banter between two or more anchors for two minutes; and a human-interest story to supposedly lighten up your day at the very end of the show — likely about a dog and cat who have learned to dance together or a two-year-old child who already knows how to play Mozart. You get the picture!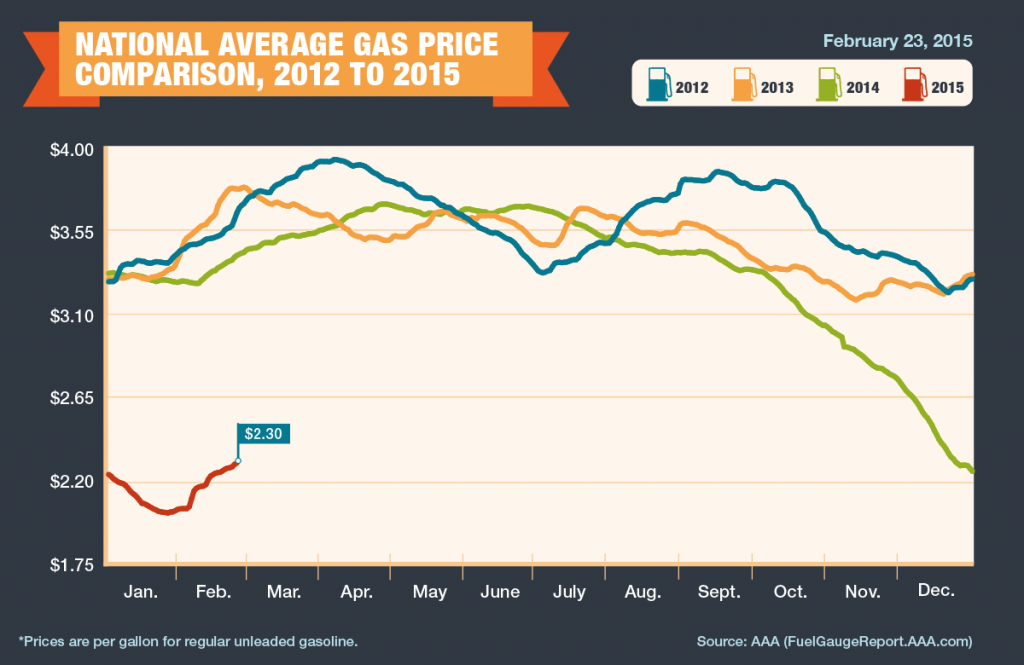 But there is good news! Many ethanol producers and advocacy groups, with enough love for America to encompass this past Valentine’s Day and the next (and of course, with concern for profits), have acknowledged that a vibrant, vigorous, loving market for E85 is possible, if E85 costs are at least 20 percent below E10 (regular gasoline) — a percentage necessary to accommodate the fact that E10 gas gets more mileage per gallon than E85. Consumers may soon have a choice at more than a few pumps.
But there is good news! Many ethanol producers and advocacy groups, with enough love for America to encompass this past Valentine’s Day and the next (and of course, with concern for profits), have acknowledged that a vibrant, vigorous, loving market for E85 is possible, if E85 costs are at least 20 percent below E10 (regular gasoline) — a percentage necessary to accommodate the fact that E10 gas gets more mileage per gallon than E85. Consumers may soon have a choice at more than a few pumps.